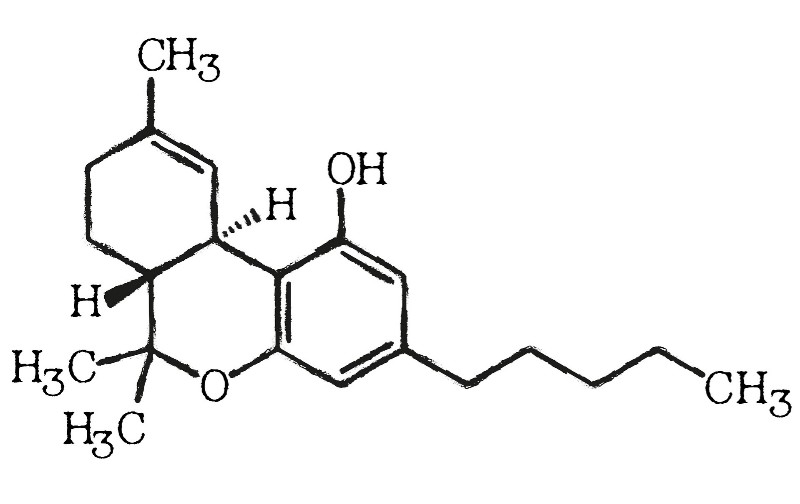
THC is one of many cannabinoid compounds found in the cannabis plant. Also known as tetrahydrocannabinol, THC is primarily responsible for the mind-altering psychological effects of the marijuana plant.
The cannabis plant secretes over 400 complex compounds in the form of resin. The most well known of which are CBD (cannabidiol) and THC. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), both compounds behave similarly to the cannabinoid chemicals formed naturally in the body.
Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabinoids are compounds that interact with the body’s Endocannabinoid system. This system is basically a network of receptors that interact with cannabinoids to regulate vital body functions.
The two cannabinoid receptors most relevant to THC are CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is associated with memory, coordination, movements, thinking, pleasure, and sensory and time perception.
THC attaches to the CB1 receptor. As such, it can affect those areas associated with memory, coordination, movement, etc. This interaction could cause negative side effects when operating machinery or driving a vehicle.
THC Composition
THC is most abundant in the reproductive glands, or buds, of the cannabis plant. Its chemical formula is C21H3002 with a molecular mass of 314.464 g/mol. THC has the exact same chemical makeup as CBD, but the arrangement of one atom is different. This seemingly insignificant difference is responsible for many variations between the two compounds.
THC vs CBD
The difference between the molecular structure of THC and CBD is responsible for the way the two substances interact with the body’s CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. Both substances bind to the CB2 receptor. However, only THC binds directly to the CB1 receptor, which creates the psychoactive experience of “being high.”
CBD does not bind to the CB1 receptor and can actually prevent THC from bonding. This lack of a bond prevents CBD from creating a “high” while still allowing it to stimulate some of the therapeutic effects of THC.
THC is still illegal in many countries and throughout the U.S. However, thanks to the 2018 Farm Bill, CBD derived from cannabis plants with less than .3 percent THC is now legal across the United States. For more detailed information about CBD, check out CBD Explained: Legality, Benefits, Dosing, & Side Effects.
Uses for THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol can be used both medicinally and recreationally. Though official studies are limited, there are still many clinical trials highlighting dozens of uses for the versatile substance.
The compound can be ingested orally in a sublingual liquid, an edible, a tincture, or via inhalation. It can be applied topically in the form of lotions, salves, and skin creams.
The substance can be used recreationally to obtain a “high,” or it can used medicinally to treat a variety of ailments. It is commonly used to treat inflammation, depression, nausea, loss of appetite, anxiety, and chronic pain.
THC and CBD can also be used to treat anxiety and pain relief in pets. Dosing varies and many veterinarians are not legally permitted to discuss using either substance for pain relief.
As such, if you choose to treat your pet with a cannabis substance, start with the lowest possible dose and carefully monitor your pet’s reaction. Slowly increase the dose based on your animal’s sensitivity and receptivity to the substance.
Side Effects of THC
A comprehensive study compiled by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) details some of the common side effects associated with THC.
Evidently, cannabis use prior to driving increases the risk of being involved in a motor vehicle accident. Further, states that have legalized the substance report more accidental cannabis overdoses in children, most often from ingesting edible THC products.
Regularly smoking cannabis is associated with chronic cough, phlegm production, and bronchitis.
The study found learning, attention, and memory are impaired immediately after cannabis use. Evidence also suggests a link between early cannabis use and lower academic achievement.
Ultimately, the study compiled by NASEM recommends more research on the effects of THC. There are many barriers to conducting thorough, accurate studies on the substance as it is still classified by the DEA as a Schedule I drug.
This classification prevents researchers from obtaining the quantity, quality, and type of cannabis products needed to advance their research.
THC Health Benefits
There are many supposed health benefits associated with THC. However, the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) advises, “Whether marijuana has therapeutic benefits that outweigh its health risks is uncertain.” Again, limited access to the plant has hindered scientific research.
There are currently three FDA-approved drugs derived from cannabinoids. Dronabinol contains a synthetic THC and is used to treat loss of appetite, weight loss, nausea, and vomiting. Marinol is another FDA-approved medicine containing synthetic THC. Epidiolex is the only FDA-approved CBD-based medication. It is used to treat rare forms of epilepsy.
Several clinical trials of THC link the substance to a decrease in spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis or spinal cord injury. These studies also showed a positive influence on pain, paraesthesia, tremor, and ataxia.
Several large clinical studies have been conducted regarding the pain-relieving properties of cannabis and THC products. Researchers linked THC to pain relief from multiple sclerosis, HIV infection, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, menstruation, chronic bowel inflammation, and neuralgia.
The positive effects of THC on glaucoma have also been widely studied. Researchers found an average of 25-50 percent reduction in intraocular pressure resulting from the use of natural and synthetic cannabinoids.
Some studies have linked THC to alleviation of depression, sleep disorders, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorders, and dysthymia. However, other studies have found the opposite effect, pointing to an increase in depression and anxiety among THC users.
Where is THC Legal?
In the United States, THC products are federally illegal and considered Schedule I substances. Individual states have been experimenting with allowing medical and/or recreational cannabis sales. Nearly 80 million Americans live in a state or jurisdiction with legalized adult-use marijuana.
Medical marijuana is legal in 33 states, the District of Columbia, Guam, and Puerto Rico.
Recreational or adult-use marijuana is now legal in ten states, and the District of Columbia. In order of when those laws were approved, the ten states are: Colorado, Washington, Alaska, Oregon, California, Maine, Massachusetts, Nevada, Vermont, and Michigan.
For more information about THC, CBD, and the science and technology behind the industry, subscribe to Cannabis & Tech Today for FREE.
Author
-

Patricia Miller is an executive editor at Innovative Properties Worldwide. She explores science, technology, and policy shaping the legal cannabis sector. Follow her work when you subscribe to Cannabis & Tech Today at cannatechtoday.com/subscribe/ or visit her website https://patriciamiller.squarespace.com/.